Probability Distribution for Flipping Four Coins
By starting Newtons method at different. Probability Rule Five The General Addition Rule How can I determine probability when picking random numbers.
A Coin Is Tossed 4 Times What Is The Probability That The Outcomes Of The Tosses Consist Of One Head And Three Tails Quora
Remember it all based on the range of the random number generator.

. The probability density function explains the normal distribution and how mean and deviation exist. We can represent the dice roll example graphically as shown below. Lets imagine a simple experiment.
The probability of a failure a tail is thus also 05. Is a frequency distribution of a binomial process for the experiment of flipping three coins where the random variable is the number of heads. For instance if the range is 1 through 9 then the probability of.
The Hats and the Monster. Then we are interested in solving for PU5T ie the probability that we are flipping the unfair coin given that we saw 5 tails in a row. The probability distribution for total distance covered in a random walk biased or unbiased will tend toward a normal distribution.
For example fair coins 50 tails 50 tails and fair dice 16 probability for each of the six faces follow uniform distributions. 66 Flipping a Random Coin. There are one hundred people standing in a circle.
Write a program BohrRadiusjava that finds the radii where the probability of finding the electron in the 4s excited state of hydrogen is zero. As for any probability distribution. So just use combinations ie.
A distribution is uniform when all of the outcomes have the same probability. Flipping many coins will result in a normal distribution for the total number of heads or equivalently total number of tails. Let U denote the case where we are flipping the unfair coin and F denote the case where we are flipping a fair coin.
The Circle of Deathkeyboard_arrow_up. Proportion of Girls and Boys. Eggs from a Building.
They count off beginning at one and ending at one hundred. If you experiment with 1 2 3 and 4 coins you find that there are always 2n possibilities where n is the number of coins. 1 - 3r4 r 2 8 - r 3 192 2 e-r2 where r is the radius in units of the Bohr radius 0529173E-8 cm.
You should be able to do the rest. Let 5T denote the event where we flip 5 heads in a row. The sum of the numbers is exactly what we want.
Just 3 heads is 8C3 the number of possibilities is 28 at least 3 heads is just 28-8C1-8C2. In my hot little hand Im holding 20 identical six-sided dice. The sample space is listed below the distribution.
The outcome variable would always have a discrete value between 1-6. Suppose one has a box of coins where the coin probabilities vary. The probability is given by.
183 Now that we know this what we have to do to. We can state the following in regards to the probability distribution table shown above-In the case of an experiment to roll a six-sided dice where the values lie in the set 123456. Since the coin is chosen randomly we know that PU PF 05.
The theory of probability originated in the attempt to describe how games of chance work so it seems fitting that our discussion of the binomial distribution should involve a discussion of rolling dice and flipping coins. In the notation that we developed in Chapter 9 this is written. Now consider Pascals triangle.
The experiment assumed that the probability of a success is 05. Five Pirates 100 Gold Coins. Since they are in a circle ONE is next to.
Calculate the probability of getting an even number if a. PO_11 O_12 O_21 O_22 R_1 R_2 C_1 C_2 and as you might imagine its a slightly tricky exercise to figure out what this probability is but it turns out that this probability is described by a distribution known as the hypergeometric distribution. On one face of each die theres a picture of a skull.
If one selects a coin from the box p the probability the coin lands heads follows the distribution gp frac1B6 6 p5 1 - p5 0 p 1 where B66 is the Beta function which will be more. The standard normal distribution is used to create a database or statistics which are often used in science to represent the real-valued variables whose distribution is not known. Solved Examples Probability.
A probability distribution is a function that assigns a probability to every possible outcome such that the probabilities add up to 1. Probability Rule Four Addition Rule for Disjoint Events Finding PA and B using Logic.
A Coin Is Tossed Ten Times How Many Possible Outcomes Are There In Total Quora
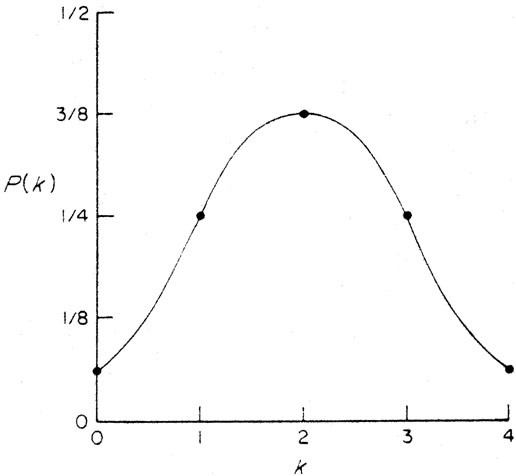
Probabilities And Probability Distributions H C Berg

Binomial Distribution Via Coin Flips Wolfram Demonstrations Project

A Coin Is Tossed 4 Times Let X Denote The Number Of Heads Find The Probability Distribut Youtube
Four Coins Are Tossed Let X Be The Random Variable Representing The Number Of Tails That Occur What Is The Probability Distribution Quora

Solved Probability Distribution For Number Of Heads Chegg Com
If You Flip A Fair Coin 4 Times What Is The Probability That You Will Get Exactly 2 Tails Socratic
What Is The Probability Of Getting 3 Heads And 1 Tail When 4 Coins Are Tossed Quora

Flipping 4 Coins Probability Youtube

That Common Misconception About Probability By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium
A Coin Is Tossed 4 Times What Is The Probability Of At Least One Tail Quora
Sum Of The Probabilities And The Mean Of A Binomial Distribution

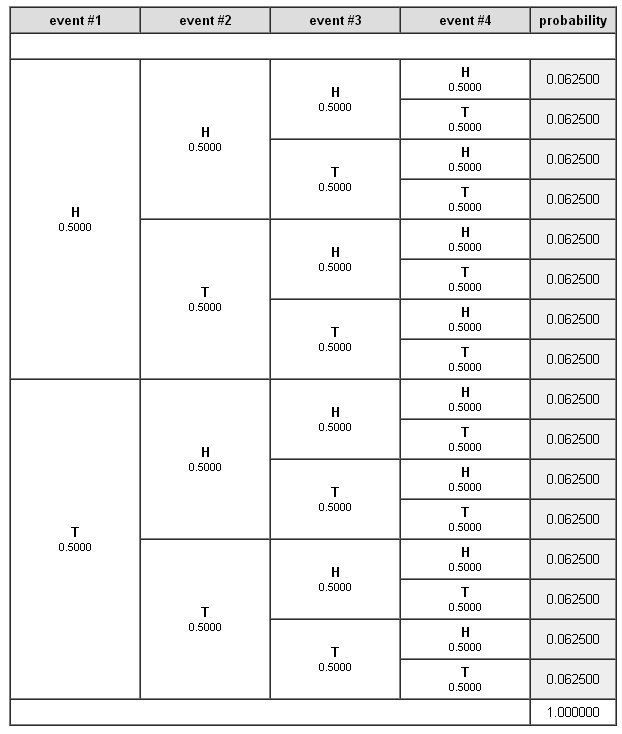
Use A Tree Diagram Showing All Possible Results When Four Fair Coins Are Tossed Then List The Ways Of Getting The Indicated Result Study Com

If Four Coins Are Tossed Find The Probability That There Shall Be Two Heads And Two Tails Youtube

Flip A Coin 4 Times Xi Number Of Heads Xi P Xi 0 1 16 1 4 16 2 6 16 3 4 16 4 1 16 Draw The Next Two Sets Of Branches Study Com
Answer In Statistics And Probability For Ely 185600
Sum Of The Probabilities And The Mean Of A Binomial Distribution


Comments
Post a Comment